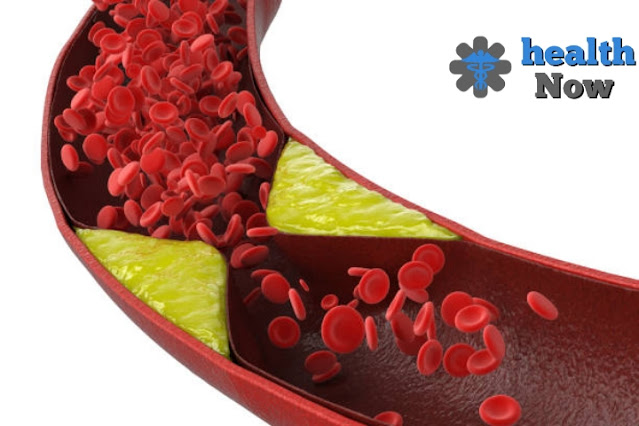
Definition of atherosclerosis.
Atherosclerosis is a slow cycle in
which substances containing fat and cholesterol amass on the conduit divider which prompts restricting of the corridor and might be totally
obstructed, Atherosclerosis is an illness brought about by the improvement of layers of greasy stores on the interior dividers of the courses.
The interaction is called calcification, since when a supply route is worked on, we find a solidifying substance, once in a while near whiteness, called appendage, which is called, The improvement of these stores prompts the gradual limiting and deterrent of bloodstream in the conduit. This sickness normally influences enormous or medium veins.
Symptoms of atherosclerosis.
You might not have side effects until the corridor is practically shut or until you have a coronary episode or stroke, imprints can likewise rely upon the thin vein or obstructed, in the accompanying outline:
1. Symptoms related to coronary arteries.
Arrhythmias, uncommon heartbeat. Agony or strain in your chest area, including your chest, arms, neck, or jaw. This is known as angina. Windedness.
2. Symptoms related to arteries that transmit blood to the brain.
- Deadness or deficiency in your arms or legs.
- Trouble talking or understanding somebody talking.
- Prolapse of the facial muscles.
- Loss of motion.
- An extreme migraine.
- One's vision issue.
3. Symptoms related to arms, legs, and pelvis arteries.
- Leg torment while strolling.
- Deadness.
4. Symptoms related to arteries that transmit blood to the kidneys.
Causes of atherosclerosis.
Main reasons.
- High fat.
- High blood pressure.
- inflammation such as arthritis or lupus.
- Obesity.
- Smoking.
1. Key risk factors.
- Cerebrovascular disease.
- Peripheral arterial diseases.
- Abdominal blood in the abdominal aortic artery.
2. Secondary risk factors.
- Elevated degrees of cholesterol and fatty substances in the blood.
- High blood pressure and aging.
- excess weight.
- Family history.
- Physical inactivity.
- insulin resistance.
- Vitamin B12 deficiency in the blood.
Complications of atherosclerosis.
- Aneurysm.
- carnage.
- Chronic kidney failure.
- Coronary heart disease or carotid artery.
- Heart attack.
- Heart failure.
- Peripheral artery disease.
- stroke.
- Unusual rhythms of the heart.
Diagnosis of atherosclerosis.
Your primary care physician will play out an actual assessment and pose inquiries about your own and your family's well-being history. You might be alluded to by an expert cardiologist. The most noticeable assessments include:
1. Blood Tests.
Your primary care physician will require blood tests to check glucose levels and cholesterol, as high glucose levels and cholesterol increment the gamble of atherosclerosis and can likewise be tried for responsive c-protein to check for a protein-related with arthritis.
2. Electrocardiogram.
This simple, painless test records the electrical signals in your heart.
3. Exercise stress test.
Expecting your signs and secondary effects happen most often during exercise, your PCP could propose this test. You'll walk around a treadmill or ride an activity bicycle while related with an ECG machine.
Because exercise makes your heart pump harder and faster than it does in most daily activities, an exercise stress test can reveal problems within your heart that might otherwise be missed.
If you are unable to exercise, you may be given a medication that mimics the effect of exercise on your heart.
4. Echocardiogram.
This test uses sound waves to show how well blood moves as the heartbeats and through the arteries, sometimes combined with an exercise stress test.
5. Ultrasound.
Your doctor may use a special ultrasound machine to measure your blood pressure at various points along your arm or leg. These measurements can help your doctor determine the degree of any blockage as well as the speed of blood flow in your arteries.
6. Ankle Index.
This test can show if you have atherosclerosis in your legs and feet. During a test, your doctor compares the blood pressure in your ankle with the blood pressure in your arm as an abnormal difference may be a sign of peripheral vascular disease, usually caused by atherosclerosis.
7. Cardiac catheterization and angiography.
This test can show assuming your coronary corridors are limited or hindered.
During this system, your PCP embeds a slim, adaptable cylinder into a vein and into your heart where color moves through the catheter. As the color fills your veins, the courses become apparent on a X-beam, uncovering areas of blockage.
8. Coronary calcium scan.
Also called a heart scan, this common test uses computerized tomography (CT) scan to create detailed images of your heart.
It can show calcium deposits in the walls of your arteries as test results are given as scores. When calcium is present, the higher the result, the greater your risk of heart disease.
9. Other imaging tests.
Your doctor may also use magnetic resonance angiography or positron emission tomography to study your arteries.
These tests can show hardening and narrowing of the large arteries as well as aneurysms.
Treatment of atherosclerosis.
 |
The most prominent treatments include:
1. Lifestyle change.
One research shows that the following lifestyle choices may reduce risks:
- Avoid or quit smoking.
- Exercise regularly.
- Healthy diet.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
2. Medication.
A specialist will recommend prescriptions that are suitable to a singular's requirements relying upon their overall wellbeing and different circumstances, as medications known as statins can assist with controlling an individual's cholesterol levels.
Different medications can bring down the pulse, decrease glucose and forestall clumps and contaminations.
Individuals ought to adhere to specialists' directions and not quite take drugs without looking for clinical counsel, as they ought to follow a sound way of life as well as use prescriptions.
3. Surgery.
At times an individual requires a medical procedure to ensure the bloodstream in his veins goes on really, and the most conspicuous choices for medical procedure incorporate what comes:
- Utilize a support point to extend veins.
- A direct detour is a medical procedure to move blood around the impacted region.
- Do a medical procedure to eliminate the aggregation of stores.
Prevention of atherosclerosis.
As per experimentally demonstrated examinations, the improvement of atherosclerosis can be forestalled by guaranteeing a solid way of life, for example:
- Quit smoking. Eat healthy foods.
- Exercise régulièrementlarly. Maintain a healthy weight.
- Blood pressure screening and preservation.
- Check and maintain cholesterol and blood sugar levels.